Training Talk Simplified
You've probably heard someone mention their macros or complain about hitting failure. Maybe you nodded along, secretly wondering what they actually meant. Fitness culture has its own vocabulary, and nobody hands you a dictionary at the gym entrance. Understanding these terms makes everything clearer—the workout programs, the coaching cues, the random advice people love sharing. Let's decode the language so you actually know what's being discussed around you.
1. Active Recovery
You know that feeling when you're convinced lying on the couch is the best medicine after leg day? Here's the twist: gentle movement actually beats complete rest. Active recovery keeps your blood flowing better between training sessions, which means less stiffness and faster bounce-back.
2. BFR
Blood flow restriction training sounds intense, but it's actually a game-changer for people rebuilding strength after injuries. By using bands or cuffs to partially restrict circulation during exercise, you can challenge your muscles with surprisingly light weights.
3. Calisthenics
The beauty of calisthenics lies in its simplicity—push-ups, squats, and pull-ups require zero equipment but deliver serious results. What makes it special is how it develops strength, mobility, and coordination simultaneously, unlike isolated machine work.
4. DB
Dumbbells force each side of your body to pull its own weight, literally. Whether you're doing presses, rows, or lunges, that single DB in your hand opens up dozens of full-body exercise possibilities that barbells simply can't replicate.
5. Eccentric
The lowering phase, where you're fighting gravity as the weight comes down, actually creates more muscle damage than the lifting part. Controlled eccentrics improve both your strength and technique because you're forcing your muscles to work hard while lengthening.
6. Failure
Training to failure means repping out until your form breaks down and you literally cannot complete another repetition safely. Most people save this intensity technique for their final set because pushing that complex every single set leads straight to burnout.
7. Gains
Performance improvements or visible muscle growth. That's what "gains" means in gym speak. Consistent training paired with proper nutrition is the only reliable formula, though people obsess over finding shortcuts. Small increases in strength or size compound faster than most beginners expect.
8. Half Rep
Targeting weak points in your range of motion is where half reps shine. Instead of completing the full movement, you're isolating a specific portion. Lifters use partials to build strength in those sticky points without loading up heavier weights.
9. Intra-Workout
What you consume during training, water, electrolytes, or simple carbs, can make or break long sessions. Energy maintenance is the goal here, especially when you're grinding through a ninety-minute workout or intense conditioning. Sometimes, just a few sips of water are enough.
10. Jacked
Visibly muscular development earns you this compliment in fitness circles. The term celebrates someone's physique progress and dedication, though it's not reserved for powerlifters alone. People achieve that jacked look through various training methods.
11. KB
A kettlebell's unique design—that handle attached to a cannonball-shaped weight—enables swinging movements that barbells and dumbbells simply can't match. These dynamic exercises build explosive power while simultaneously challenging your conditioning, making them incredibly efficient for athletes short on time.
12. Lactic Acid
That burning sensation flooding your quads during high-rep squats? That's lactic acid accumulating when your muscles are working too hard for oxygen delivery to keep pace. Your body naturally clears this metabolic byproduct after you finish exercising.
13. Macros
Protein, carbohydrates, and fats. These three nutrients fuel everything from your morning run to your evening deadlift session. Tracking them gives you precision control over reaching specific fitness goals, whether that's building muscle or dropping body fat.
14. Negatives
Strength and control skyrocket when you focus exclusively on the slow lowering portion of each lift. Many lifters discover that emphasizing negatives helps them break through frustrating plateaus where progress has completely stalled. Even weights that felt manageable suddenly become brutal challenges.
 @marcuschanmedia | IG on Pexels
@marcuschanmedia | IG on Pexels
15. Olympic Weightlifting
The snatch and clean demand an explosive combination of strength, speed, and technical precision that few other movements require. Practiced competitively worldwide, these lifts look intimidating to outsiders but become surprisingly enjoyable once you learn the fundamental mechanics.
 Sandro Halank, Wikimedia Commons on Wikimedia
Sandro Halank, Wikimedia Commons on Wikimedia
16. Parasympathetic Nervous System
Deep breathing activates your body's built-in relaxation system, shifting you out of fight-or-flight mode after intense training. This system slows your heart rate and initiates the recovery process naturally, without any supplements or special equipment.
17. Recovery
Preventing injury and chronic fatigue hinges entirely on how well you recover between sessions. Rest and proper nutrition form the foundation, though many people prioritize training volume. Athletes who improve fastest often treat recovery with the same seriousness as their workouts.
18. Scale
Daily weight fluctuations happen for countless reasons—hydration, sodium intake, hormones, digestion—none of which reflect actual fat loss or muscle gain. The number staring back at you measures only one narrow metric while ignoring strength gains, improved endurance, and body composition changes.
19. Tabata
Four minutes of properly executed Tabata intervals can leave you more exhausted than a thirty-minute steady-state cardio session. This high-intensity format alternates maximum effort bursts with minimal rest periods, creating a time-efficient workout that delivers serious results.
 Antoni Shkraba Studio on Pexels
Antoni Shkraba Studio on Pexels
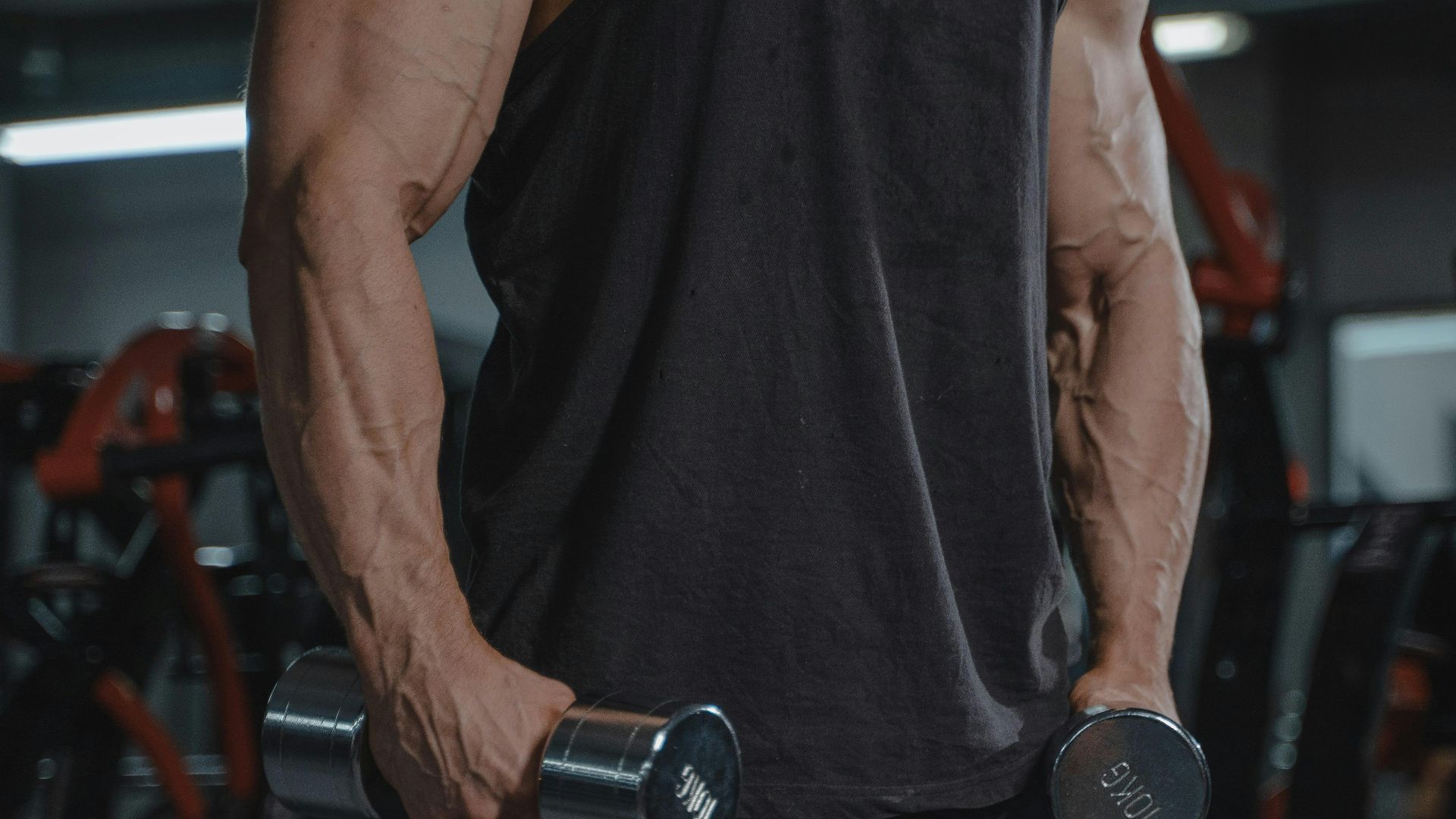
20. Vascularity
Genetics determines much of how prominently your veins appear, regardless of how hard you train or how lean you get. Low body fat combined with increased blood flow during training makes veins more visible. Regular training increases vascularity over time.

























