Keeping A Track Of Sodium Intake
Salt quietly governs far more than taste—it regulates how your body retains water and fuels nerve and muscle function. But when sodium intake tips too far in either direction, your body reacts in surprising ways that often go unnoticed until symptoms build up. While excessive salt gets most of the blame, not getting enough can be just as risky. Let’s start with the signs that your salt intake might be higher than your body can handle.
1. Persistent Puffiness Under Your Eyes
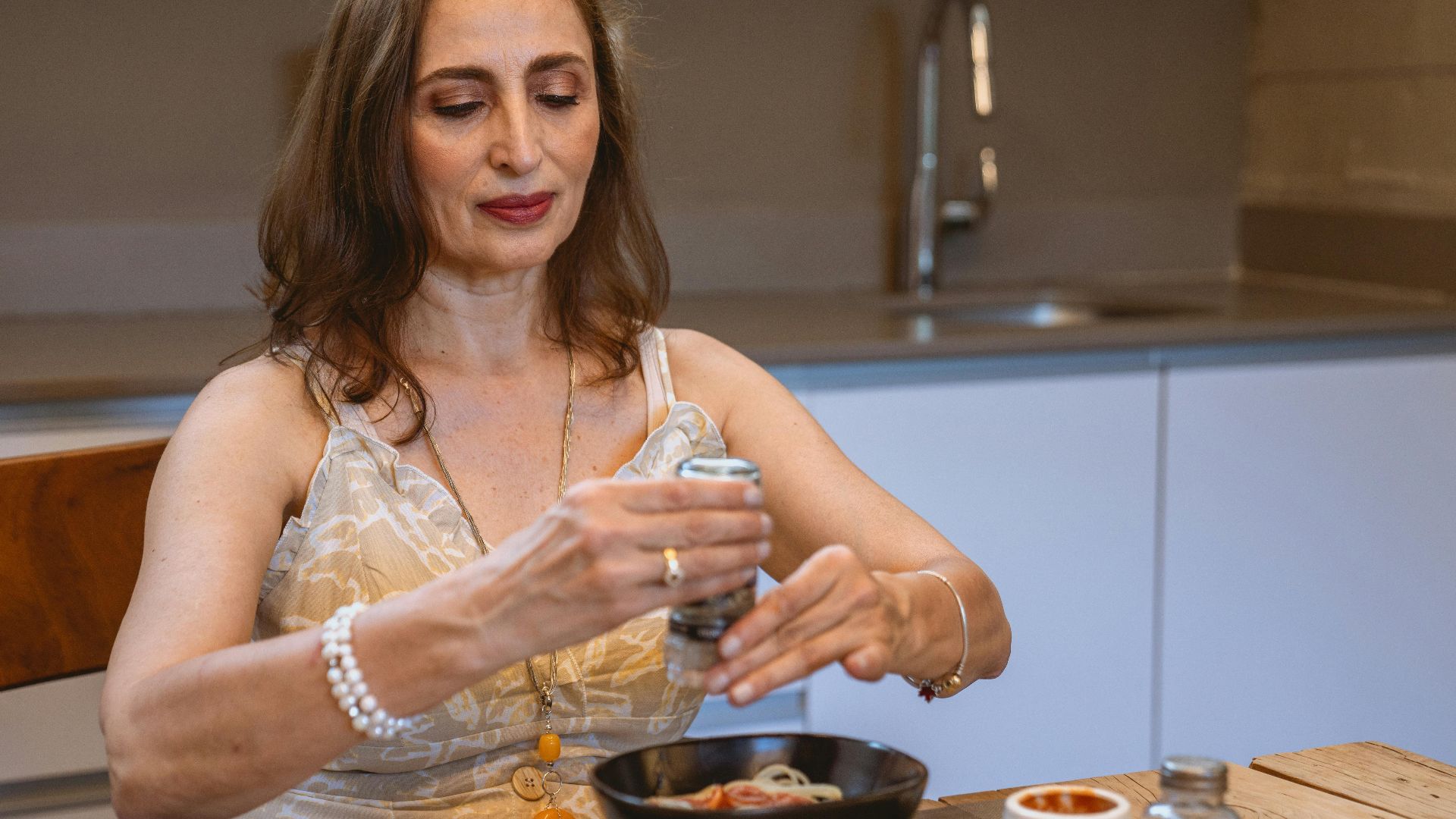
If you often wake up with swollen eyelids, your salt intake might be to blame. Too much sodium makes the body retain water, especially around delicate facial tissues—causing puffiness, particularly noticeable after salty dinners or late-night snacks.
 Andrew Patrick Photo on Pexels
Andrew Patrick Photo on Pexels
2. Frequent Intense Thirst After Meals
Feeling extremely thirsty after meals may indicate excess salt intake. Sodium draws water out of your cells, leaving you dehydrated despite drinking fluids. This imbalance can trigger dry mouth, fatigue, and frequent urination shortly after eating.
3. Sudden Unexplained Weight Fluctuations
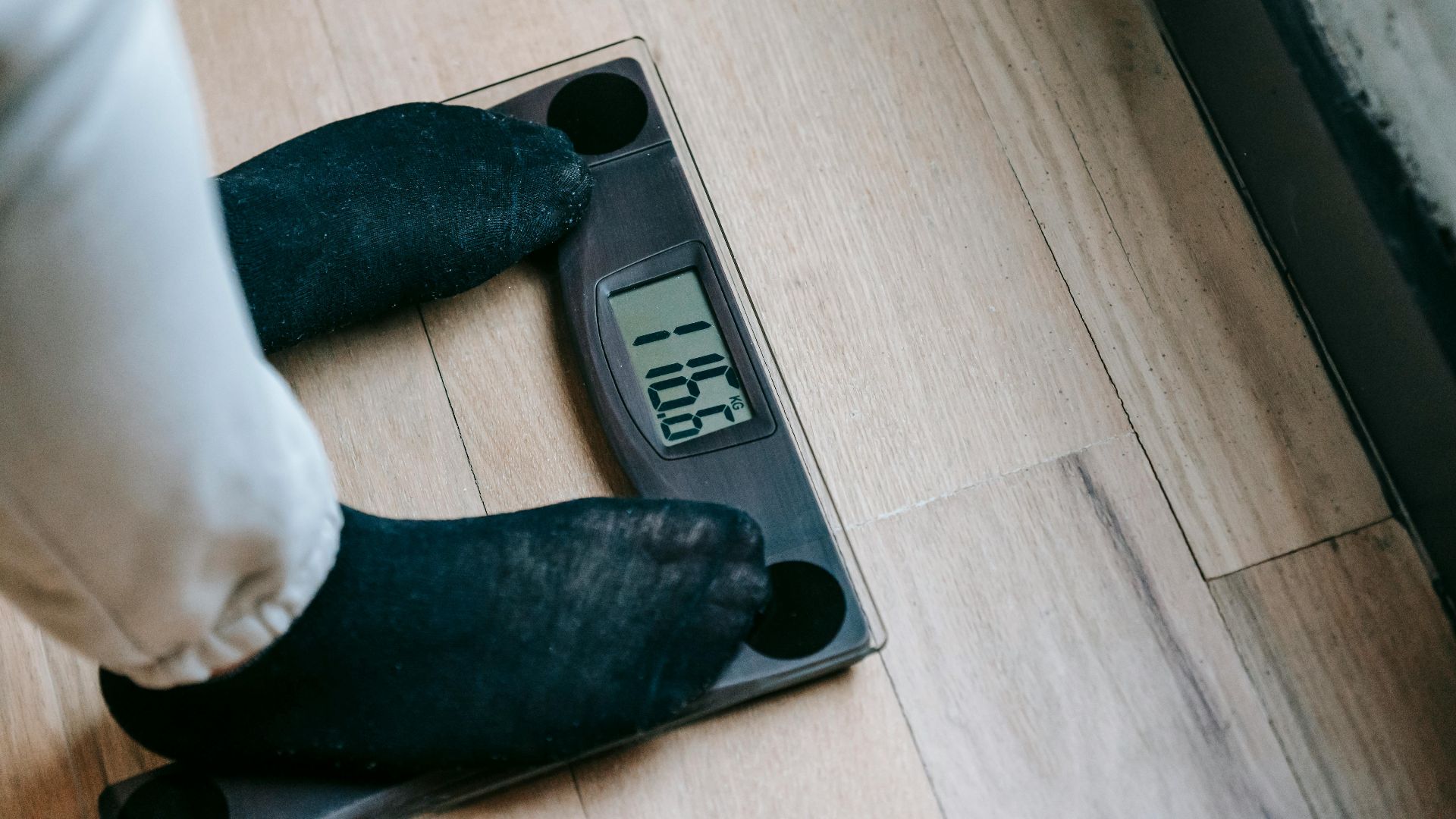
Notice your weight jumping up overnight? High salt intake can cause water retention that leads to temporary weight gain. This sudden shift is water weight, making your clothes feel tighter without any actual body changes.
4. Chronic Bloating In The Abdomen
That uncomfortable tightness after eating could be sodium overload. Salt makes the body cling to fluid, and the abdomen often bears the brunt. If you feel puffy or heavy after even light meals, your salt habits are worth rethinking.
5. Headaches Centered Around Temples
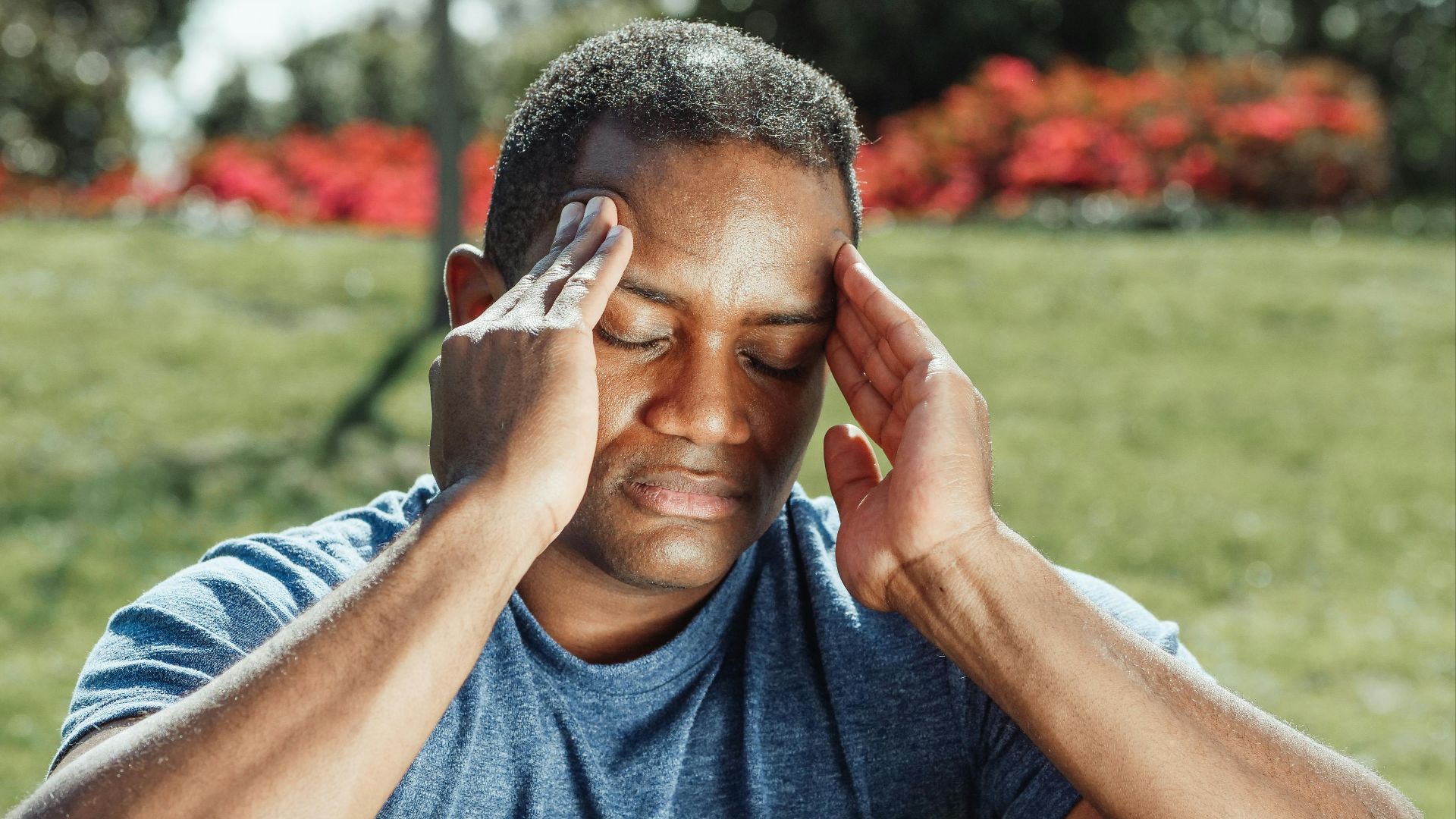
A dull pressure creeping across your temples may have more to do with diet than stress. High-salt meals can trigger dehydration, tighten blood vessels, and spark headaches. Keeping a food diary can help reveal whether your pain follows particularly salty foods.
6. Consistently Foamy Urine
Foamy urine can be a red flag that the kidneys are working overtime. Too much salt strains these vital organs, sometimes leading to protein leakage. It is a sign they’re struggling to filter waste and maintain fluid balance efficiently.
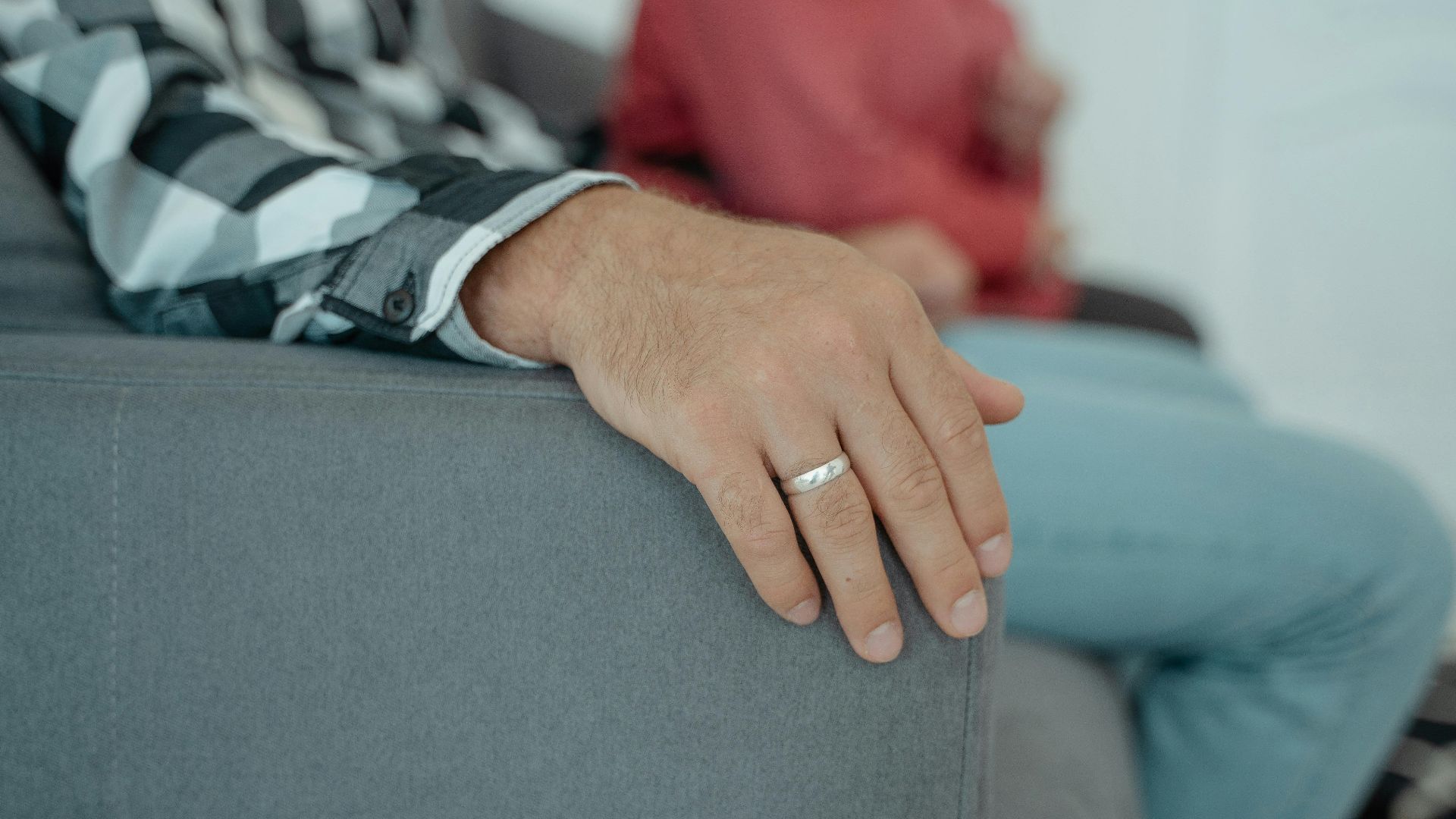
7. Swollen Hands That Leave Ring Indentations
If your fingers feel like they’ve outgrown your rings, sodium may be the culprit. High salt levels cause fluid buildup in extremities, which makes jewelry and shoes tighter. Try reducing processed foods for a week, and you might be surprised at how quickly the swelling subsides.
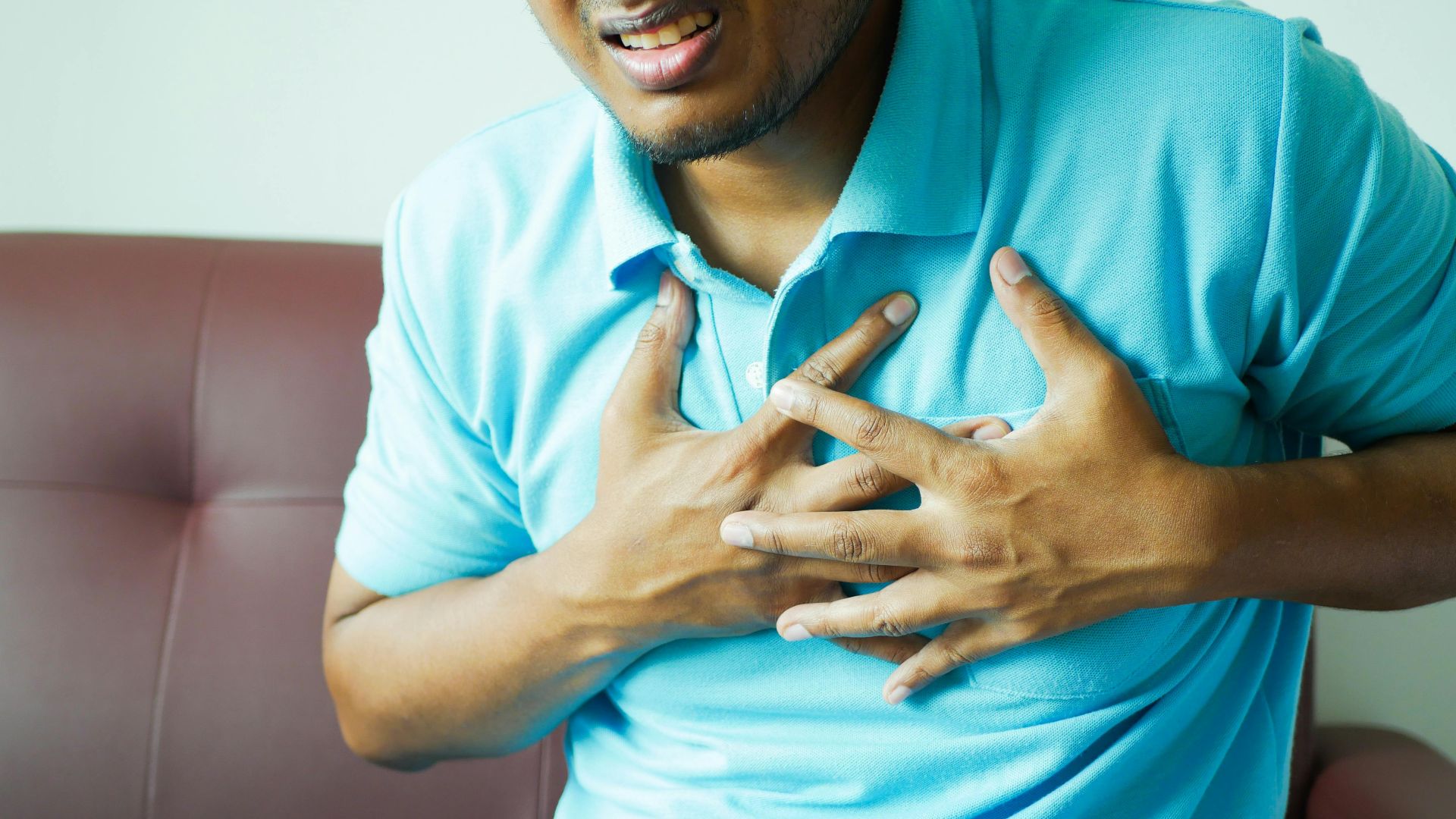
8. Heart Palpitations After Salty Foods
Feeling your heart race after eating chips or fast food? Excess salt increases blood volume and makes your heart pump harder. These palpitations can feel like pounding or fluttering and are the body’s way of signaling stress on the cardiovascular system.
9. Fatigue Despite Adequate Sleep
You might think eight hours of sleep guarantees energy, but excess salt can sabotage rest. High sodium disrupts fluid balance and can cause nighttime bathroom trips that fragment deep sleep. Swap salt-heavy dinners for lighter options, as it can restore your morning alertness.
10. Blood Pressure Spikes Above 130/80
A diet high in salt can silently raise your blood pressure over time. When sodium causes fluid buildup, the heart must work harder to pump blood, which pushes readings above the healthy range of 130/80 mm Hg and increases heart disease risk.
But while too much salt can quietly wreak havoc on your body, cutting it out completely isn’t the answer either. A severe lack of it can trigger some of these warning signs.
1. Frequent Muscle Cramps During Normal Activity
When muscles suddenly tighten or twitch mid-activity, the salt levels could be slipping. Sodium works hand in hand with potassium to control muscle movement. Without proper balance, your muscles misfire to cause spasms during the most ordinary movements.
2. Unusually Dry Skin Despite Hydration
Dry, flaky skin can show up even when you drink enough water. Low sodium throws off how your cells hold moisture, and that imbalance affects fluid regulation. It’s the body’s way of showing it needs steadier salt levels.
 Anastasiia Lopushynska on Pexels
Anastasiia Lopushynska on Pexels
3. Sudden Dizziness When Standing
That spinning sensation when you rise from a chair isn’t always due to dehydration. Sodium helps maintain stable blood pressure, and when it drops too low, blood flow to your brain momentarily falters. This causes dizziness, which is especially noticeable after long heat exposure.
4. Nausea Without A Clear Food Cause
The mineral supports digestion and fluid balance, so when it’s lacking, the digestive system can go haywire. This imbalance may cause nausea or even vomiting, as these symptoms are often mistaken for food-related issues. So, try having homemade food with adequate salt.
5. Difficulty Concentrating On Tasks
Struggling to focus or think clearly could have more to do with a sodium imbalance. The brain’s neurons rely on sodium to transmit signals smoothly. When that flow is disrupted, “brain fog” sets in and slows thought processes until balance is restored.
6. Unexplained Irritability
Mood swings that come out of nowhere may not be emotional at all. Sodium influences neurotransmitters that regulate calmness and alertness. When it dips, your nerves literally fire differently to cause irritability that can easily be mistaken for anxiety or emotional burnout.
7. Low Blood Pressure Causing Weakness Episodes
If weakness or faintness hits you randomly, low blood pressure could be the culprit, and sodium plays a major role here. The mineral helps retain water in your bloodstream. When levels fall, blood pressure drops, leaving you momentarily powerless.
8. Tremors In Severe Sodium Deficiency
While rare, extremely low sodium can affect the brain’s electrical activity to trigger seizures. It’s a critical sign that your body’s salt balance has plummeted too far. This isn’t something to monitor casually—it demands immediate medical care to prevent serious neurological damage.
9. Sleep Disturbances At Night
If your nights are restless despite being tired, your sodium levels might be to blame. This mineral helps stabilize nerve and muscle signals that promote relaxation. When deficient, you might wake repeatedly.
10. Loss Of Appetite Despite Energy Requirements
Sometimes, your body’s hunger cues shut down even when you clearly need fuel. Low sodium can interfere with digestive enzymes and appetite regulation, making food seem unappealing. As sodium levels normalize, your natural hunger often returns.
KEEP ON READING

20 Natural Ways You Can Boost Your Immune System

20 Ways To De-stress & Relax After Work

The 10 Most Common Diseases & The 10 Most Rare