From Restless Nights To Restful Sleep
If you've been waking up feeling groggy or struggling with constant fatigue, it could be more than just a bad night’s sleep. The problem might be sleep apnea, a common condition that impacts your quality of rest. Identifying and addressing the issue can transform not just your nights, but your entire day. Let's first look at some key indicators that you have sleep apnea, as well as proven strategies to help you breathe easier and wake up refreshed.
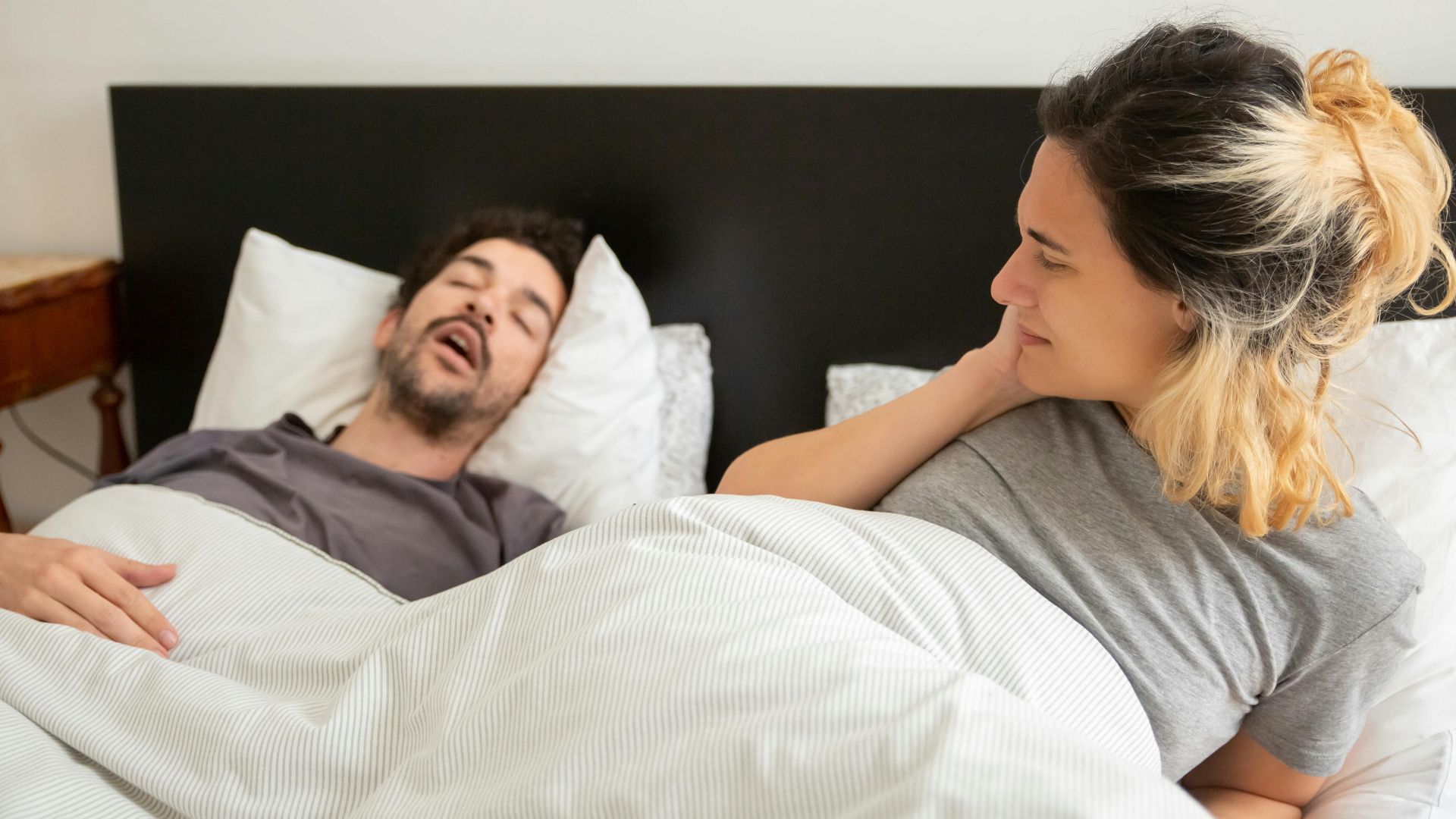
1. Loud, Chronic Snoring
While not everyone who snores has this condition, if it’s persistent and disruptive, it could signal a deeper issue. Some people snore so loudly that it disturbs others in different rooms. And in some cases, no snoring is heard at all, yet sleep apnea persists.
2. Nighttime Sweating
Waking up drenched in sweat might seem like a result of a hot room, but it could also signal sleep apnea. The body's response to oxygen deprivation during sleep often triggers night sweats. These sweats are sometimes mistaken for menopause or other conditions, but are more commonly linked to sleep apnea's disruptive nature.
3. Pauses In Breathing Observed By Others
When your breathing stops for several seconds during the night, it’s a potential sign of sleep apnea. Often noticed by bed partners, these pauses can happen multiple times throughout the night. Interestingly, many people with sleep apnea don’t realize their breathing has paused until someone tells them.
4. Morning Headaches
Waking up with a headache might be something you brush off, but when it happens regularly, it could indicate sleep apnea. These headaches are linked to poor oxygen levels during the night, which strain the body and result in tension.
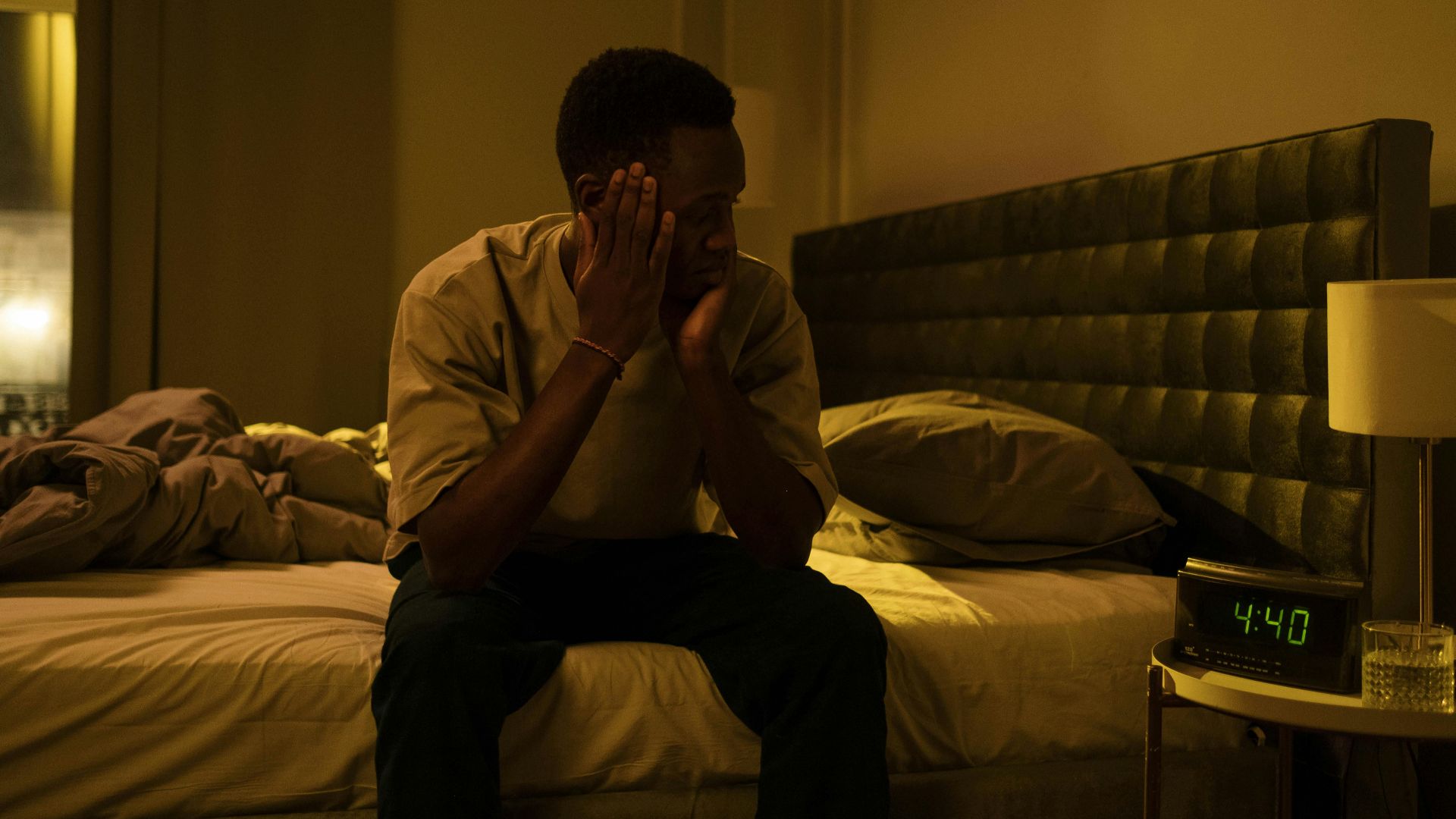
5. Excessive Daytime Sleepiness
It can be frustrating when you’ve slept a full night, yet still feel exhausted throughout the day. This is a hallmark symptom. The interruptions in your sleep cycle leave your body unrested, making it difficult to stay alert and focused.
6. Difficulty Concentrating
Are you struggling to stay focused at work or during conversations? Sleep apnea may be to blame. The lack of quality sleep affects brain function, which makes it hard to concentrate or complete tasks. As a result, memory and focus tend to decline.
7. Irritability Or Mood Swings
Sleep apnea can also increase mood swings or even anger. Poor sleep quality messes with emotional regulation and makes you more prone to snapping or feeling down. Sometimes, these mood changes are mistaken for depression or anxiety.
8. Dry Mouth Or Sore Throat
Waking up with either a dry mouth or sore throat is often a sign that you’ve been breathing through your mouth all night. For those with sleep apnea, the airway obstruction forces the body to rely on mouth breathing, which leads to dryness and irritation.
9. Frequent Nighttime Urination
Since you find yourself waking up multiple times a night to use the bathroom, it could be nocturia. That symptom is common in people with sleep apnea. These interruptions in sleep affect the body’s regulation of fluid balance, causing frequent trips to the bathroom.
10. Restless Sleep Or Frequent Awakenings
Waking up three, four, or even ten times per night leaves you exhausted by morning. What feels like insomnia often stems from repeated breathing interruptions. Your brain briefly rouses you to restart normal respiration. The result: logging plenty of hours in bed while getting minimal restorative sleep.
Fortunately, there are effective solutions to help you breathe easier and sleep better. Let’s check out the practical steps that can make all the difference in restoring your rest and well-being.
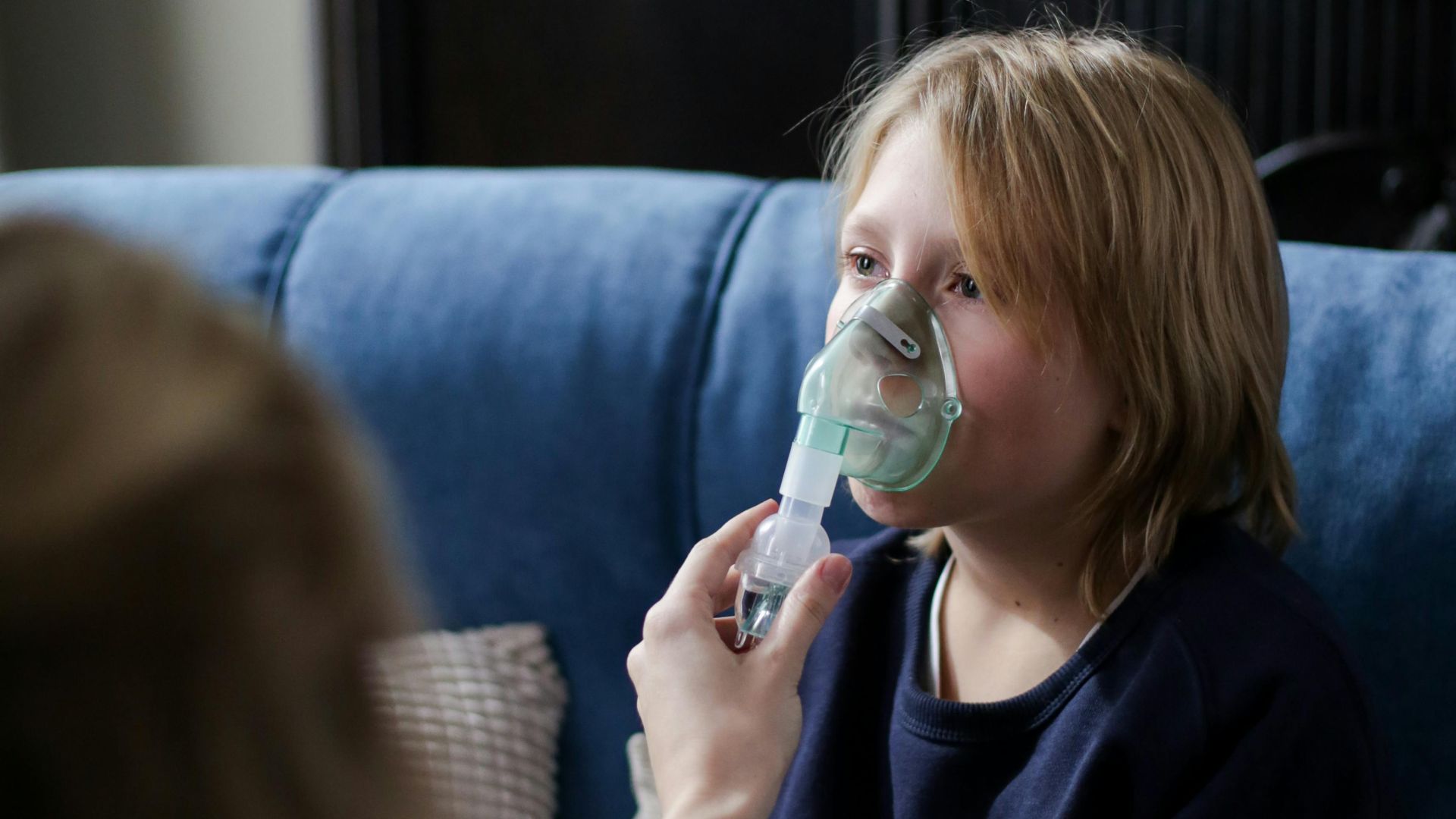
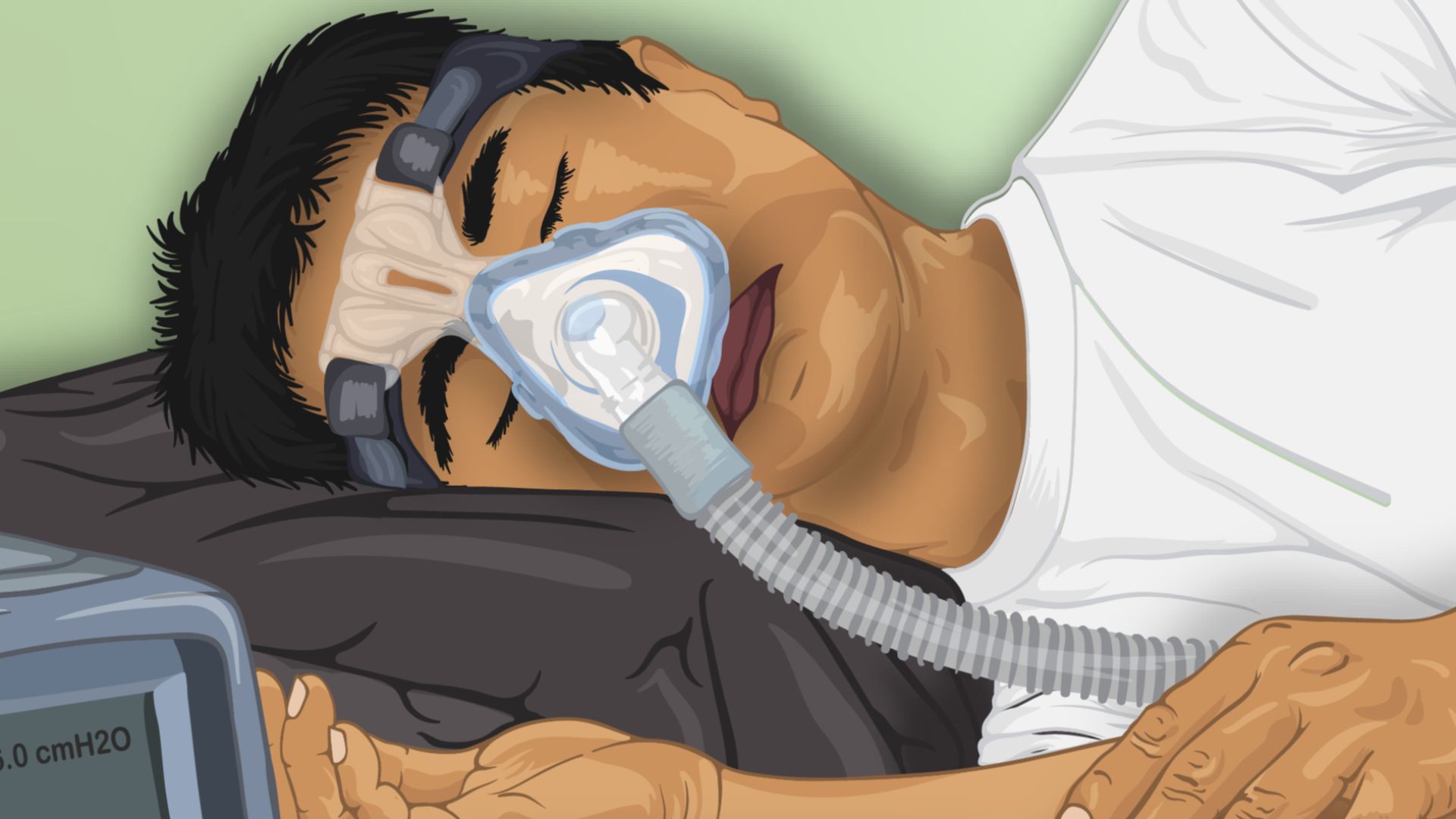
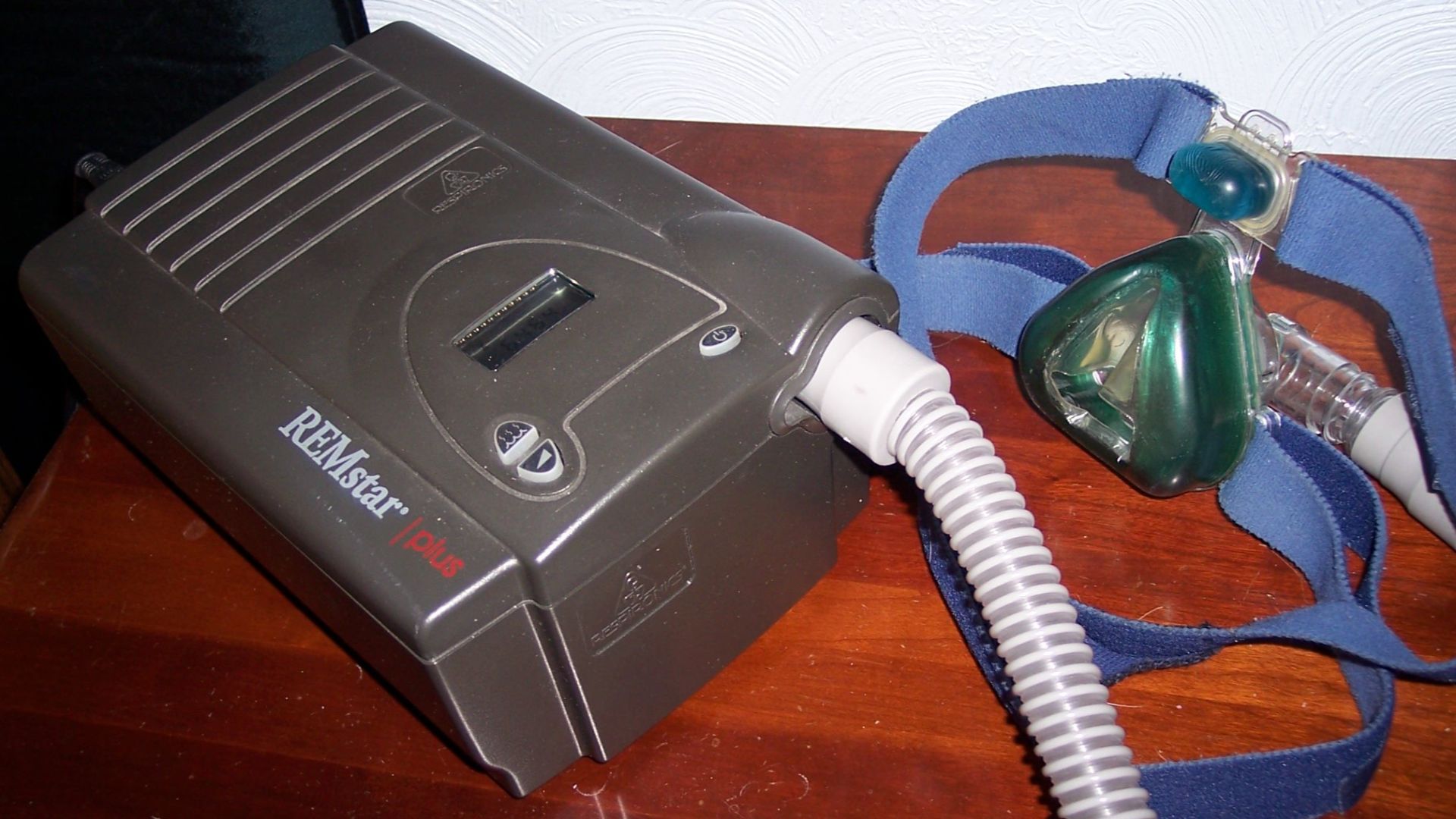
1. Use Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
The CPAP machine offers a steady flow of air to keep the airway open. It’s considered the gold standard for treating moderate to severe cases. With modern models offering features like auto-adjusting pressure and heated humidification, the CPAP has become a lot more comfortable for many users.
 https://www.myupchar.com/en on Wikimedia
https://www.myupchar.com/en on Wikimedia
2. Try Bilevel Or Auto-Adjusting Airway Devices
When a standard CPAP isn’t comfortable or effective enough, bilevel positive airway pressure (BPAP) devices and auto-CPAPs come into play. BPAP adjusts the pressure differently for inhaling and exhaling, while auto-CPAPs monitor and adjust pressure throughout the night.
 Mosquitopsu at English Wikipedia on Wikimedia
Mosquitopsu at English Wikipedia on Wikimedia
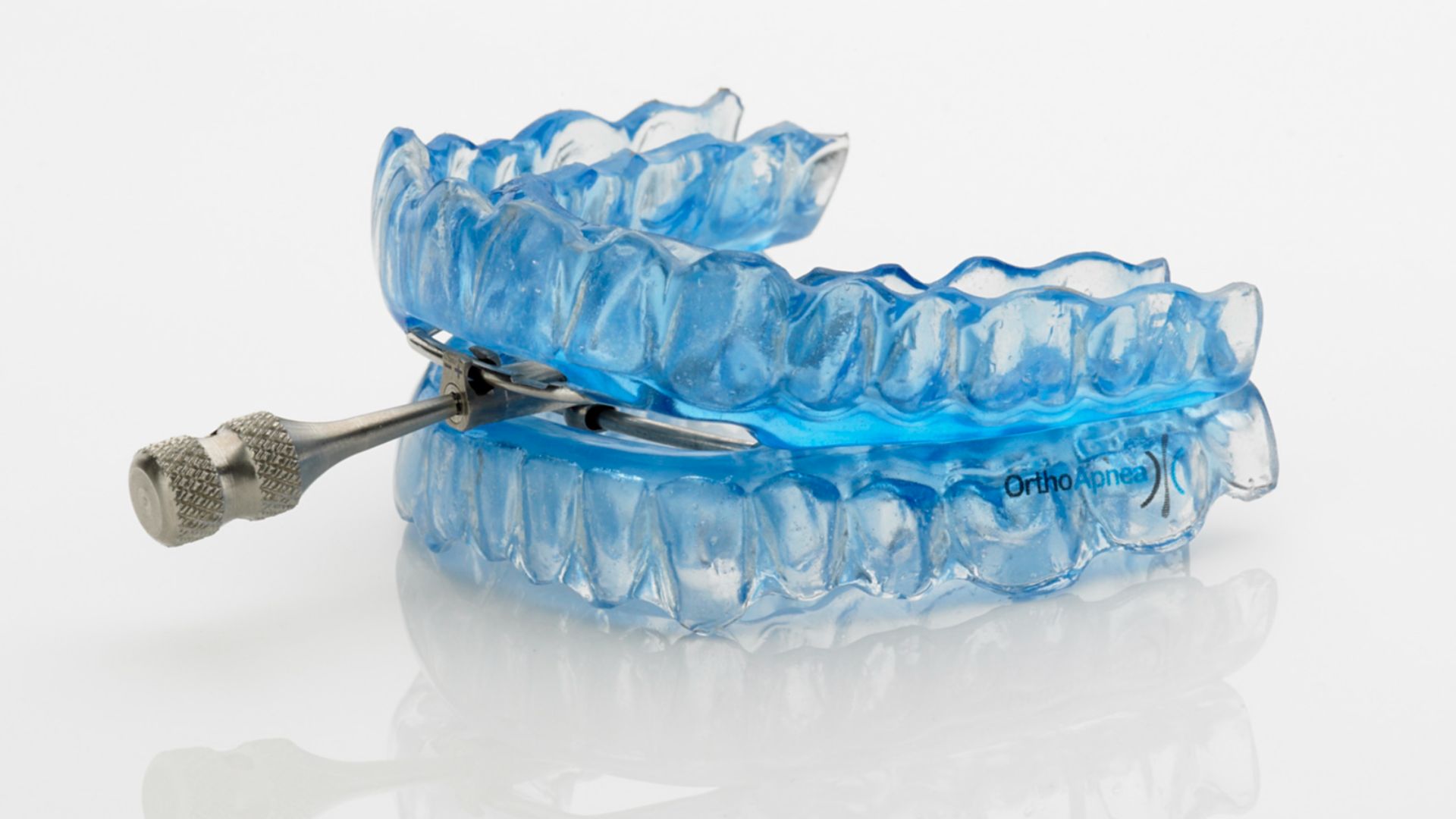
3. Wear A Custom Oral Sleep Appliance
For every sleep apnea sufferer who can't tolerate a CPAP, a custom oral appliance might be the solution. These mouthguards work by moving the jaw forward to keep the airway open. They're easy to wear and are fitted by a dentist. However, regular follow-ups are necessary.
4. Consider Upper-Airway Surgery For Blockage
Surgery might be an option for those who’ve tried CPAP or oral devices without success. Procedures can remove or shrink tissue blocking the airway, such as reshaping the soft palate or removing tonsils. While surgery can be highly effective, the recovery time and outcomes vary depending on the procedure.
5. Use Oxygen or Adaptive Servo-Ventilation Support
For certain types of sleep apnea, like central sleep apnea, supplemental oxygen may be recommended to help ensure adequate oxygen levels throughout the night. Adaptive servo-ventilation (ASV) devices can also adjust airflow in response to your unique breathing patterns. These devices are particularly helpful when breathing patterns fluctuate during sleep.
6. Begin A Structured Weight-Loss Program
Losing weight can have a significant impact on sleep apnea symptoms by reducing fat deposits around the upper airway. A structured weight-loss program may help reduce the severity and improve sleep quality. It also decreases the risk of other health problems.
7. Practice Positional Therapy
Positional therapy encourages sleeping on your side to help prevent these episodes. Some people use special pillows or even sew a tennis ball into their pajamas to remind themselves to avoid sleeping on their back. This simple method can sometimes make a big difference in reducing sleep disruptions.
8. Do Oropharyngeal Exercises
Oropharyngeal exercises mainly focus on strengthening the muscles in your mouth and throat to help keep the airway open during sleep. While these exercises can help reduce mild sleep apnea symptoms, they aren’t a substitute for primary treatments like CPAP.
9. Avoid Alcohol, Sedatives, And Tobacco Use
Certain substances, like alcohol and sedatives, relax the muscles in your throat to make it easier for the airway to collapse during sleep. Tobacco use increases inflammation in the airway and worsens sleep apnea symptoms. Avoiding these substances improves sleep and promotes better overall health.
10. Treat Nasal Congestion And Chronic Allergies
Nasal congestion or chronic allergies can worsen sleep apnea by blocking the airway. Treating these conditions can make breathing easier at night. By using nasal sprays or allergy medications before bed, you can improve airflow, and adding a HEPA filter to your bedroom can also reduce allergy triggers.